Unable to understand written words not aphasia – In the realm of language comprehension, the inability to understand written words, a condition distinct from aphasia, presents a captivating puzzle. This condition, often overlooked, warrants exploration to unravel its complexities and identify effective interventions.
Word comprehension, a cornerstone of reading and communication, involves a symphony of cognitive processes, including memory, attention, and visual processing. Difficulties in word comprehension manifest in various ways, from stumbling over unfamiliar words to struggling with the meaning of complex sentences.
Understanding the Concept of Word Comprehension

Word comprehension is the cognitive process of understanding the meaning of written words. It involves a complex interplay of cognitive functions, including memory, attention, and language processing. When individuals read, they encounter a string of letters that must be decoded into words and then into meaningful units of language.
Cognitive functions such as memory and attention play a crucial role in word comprehension. Memory allows individuals to store and retrieve information about words, including their spelling, pronunciation, and meaning. Attention enables individuals to focus on the task of reading and to ignore distractions.
Difficulties in word comprehension can manifest in various ways. Individuals may have difficulty recognizing or pronouncing words, understanding the meaning of words, or recalling the meaning of words they have previously encountered.
Differential Diagnosis of Word Comprehension Deficits

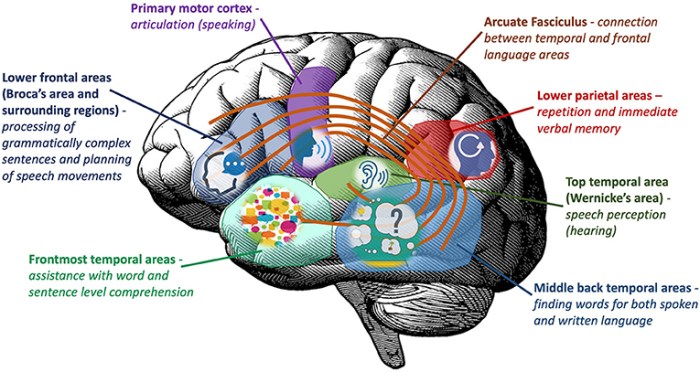
Word comprehension difficulties must be differentiated from aphasia, a language disorder that affects the ability to produce and understand language. Aphasia can result from damage to the brain areas responsible for language processing, such as Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area.
Other potential causes of word comprehension deficits include visual processing disorders, attention deficits, and cognitive impairment. Visual processing disorders can make it difficult for individuals to recognize words, while attention deficits can interfere with the ability to focus on the task of reading.
A thorough diagnostic evaluation is essential to determine the underlying cause of word comprehension deficits. This evaluation may include a medical history, neurological examination, and cognitive testing.
Cognitive Assessment of Word Comprehension

| Cognitive Test | Cognitive Function Measured |
|---|---|
| Word Recognition Test | Ability to recognize and pronounce words |
| Word Comprehension Test | Ability to understand the meaning of words |
| Word Recall Test | Ability to recall the meaning of words |
| Semantic Priming Test | Ability to activate word meanings in memory |
These tests typically involve tasks such as reading aloud words, matching words to pictures, or answering questions about the meaning of words.
Treatment Strategies for Word Comprehension Difficulties
- Phonological Awareness Training:Improves the ability to recognize and manipulate the sound structure of words.
- Vocabulary Instruction:Teaches new words and improves understanding of existing vocabulary.
- Comprehension Strategy Instruction:Teaches strategies for understanding written text, such as previewing, predicting, and summarizing.
- Metacognitive Strategy Instruction:Teaches individuals to monitor their own comprehension and to use strategies to improve it.
Treatment should be tailored to the individual’s specific needs and may involve a combination of these approaches.
FAQ Explained: Unable To Understand Written Words Not Aphasia
What are the common symptoms of word comprehension difficulties?
Individuals may experience difficulty reading unfamiliar words, understanding the meaning of sentences, or following written instructions.
How is word comprehension assessed?
Cognitive tests evaluate various aspects of word comprehension, such as vocabulary, reading fluency, and sentence comprehension.
What is the difference between word comprehension difficulties and aphasia?
Aphasia affects language production and comprehension, while word comprehension difficulties specifically impair the ability to understand written words.