Embark on an illuminating journey into the captivating world of life’s diversity with the six kingdoms of life review sheet answer key. This comprehensive guide unveils the intricate characteristics, evolutionary relationships, and ecological interactions that define the six kingdoms of life, providing a profound understanding of the intricate tapestry of life on Earth.
Delve into the unique attributes of Archaea and Bacteria, explore the fascinating complexities of eukaryotes, and trace the evolutionary history of life through a phylogenetic tree. Discover the ecological dynamics that shape interactions between kingdoms, and unravel the profound importance of each kingdom to the functioning of ecosystems and human society.
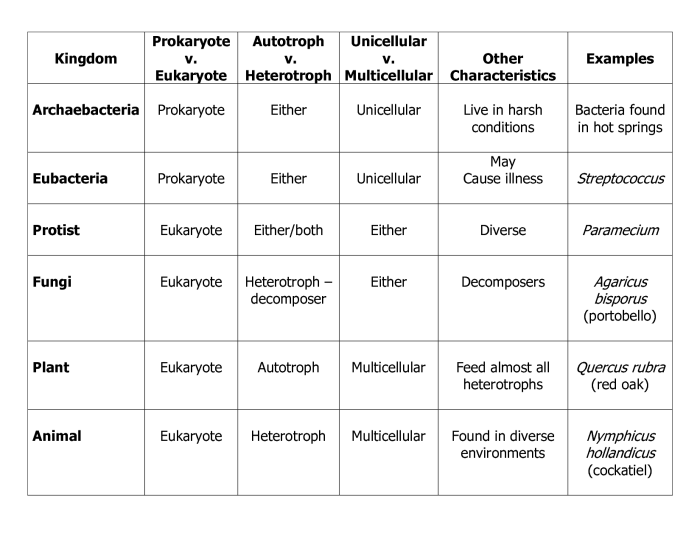
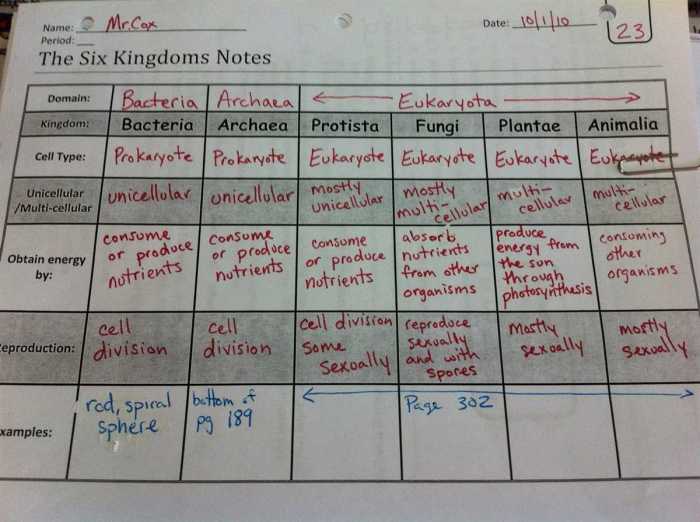
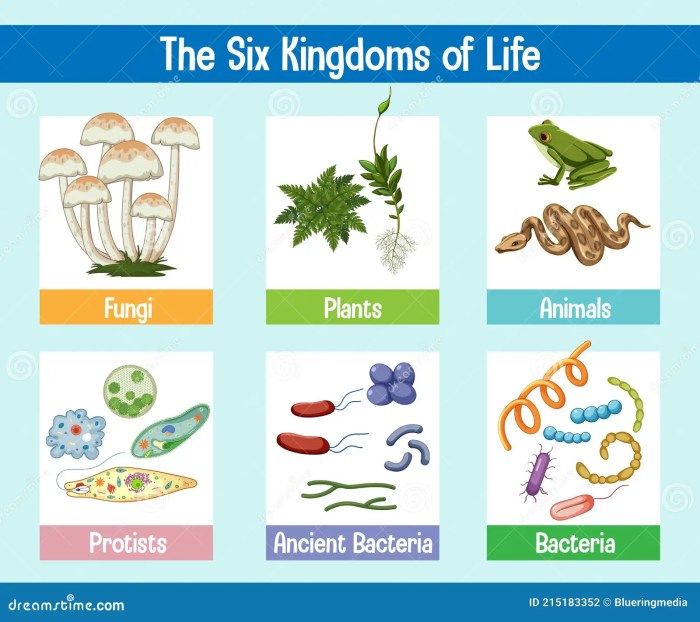
Six Kingdoms of Life Overview

The six kingdoms of life are a classification system used to organize the diversity of life on Earth. Each kingdom represents a group of organisms that share common characteristics and evolutionary relationships.
The six kingdoms are:
- Bacteria
- Archaea
- Protista
- Fungi
- Plantae
- Animalia
Each kingdom has unique characteristics that distinguish it from the others. These characteristics include cell structure, mode of nutrition, and reproduction.
Bacteria
Bacteria are single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are prokaryotes, meaning they have a simple cell structure. Bacteria are found in all environments on Earth, from the deepest oceans to the highest mountains.
Bacteria are essential for the functioning of ecosystems. They play a role in nutrient cycling, decomposition, and the production of oxygen.
Archaea
Archaea are also single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. However, they are distinct from bacteria in their cell structure and biochemistry.
Archaea are found in extreme environments, such as hot springs, deep-sea vents, and acidic lakes. They are able to survive in these harsh conditions due to their unique adaptations.
Archaea play a role in the cycling of carbon and nitrogen in the environment.
Protista
Protists are a diverse group of eukaryotes that include algae, protozoa, and slime molds. They are single-celled or multicellular organisms that have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
Protists are found in all environments on Earth. They are important producers in aquatic ecosystems and play a role in the food chain.
Fungi
Fungi are eukaryotes that include yeasts, molds, and mushrooms. They are heterotrophs, meaning they obtain their nutrients from other organisms.
Fungi are found in all environments on Earth. They play a role in nutrient cycling and decomposition.
Plantae
Plantae are eukaryotes that include mosses, ferns, gymnosperms, and flowering plants. They are autotrophs, meaning they produce their own food through photosynthesis.
Plantae are found in all environments on Earth. They are the primary producers in terrestrial ecosystems and provide food and shelter for other organisms.
Animalia, The six kingdoms of life review sheet answer key
Animalia are eukaryotes that include insects, fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. They are heterotrophs, meaning they obtain their nutrients from other organisms.
Animalia are found in all environments on Earth. They play a role in the food chain and in the dispersal of seeds.
FAQ Section: The Six Kingdoms Of Life Review Sheet Answer Key
What are the six kingdoms of life?
The six kingdoms of life are Archaea, Bacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
How do Archaea differ from Bacteria?
Archaea differ from Bacteria in their cell wall structure, membrane lipids, and metabolic pathways.
What is the role of protists in the environment?
Protists play vital roles as primary producers, consumers, and decomposers in various ecosystems.