The properties of life mastering biology – The Properties of Life: Mastering Biology sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental principles of life, exploring the essential characteristics that define living organisms and the intricate mechanisms that govern their existence.
Through a series of engaging chapters, this text unravels the mysteries of the cell theory, the building blocks of life, and the processes that sustain them. From the smallest microorganisms to the most complex ecosystems, The Properties of Life: Mastering Biology provides a captivating journey through the wonders of the living world.
The Cell Theory
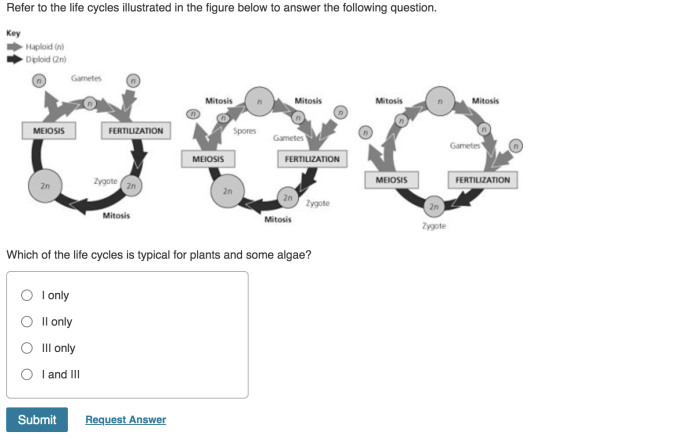
The cell theory is a fundamental concept in biology that states that all living organisms are composed of cells, that cells are the basic unit of life, and that new cells arise only from existing cells.
The three main tenets of the cell theory are:
- All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
- The cell is the basic unit of life.
- New cells arise only from existing cells.
The cell theory has been used to advance our understanding of biology in many ways. For example, it has helped us to understand how organisms grow, reproduce, and repair themselves. It has also helped us to develop new treatments for diseases.
However, the cell theory does have some limitations. For example, it does not apply to viruses, which are not cells. Additionally, the cell theory does not explain how life originated.
The Properties of Life
| Property | Definition | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Organization | Living organisms are highly organized, with their components arranged in a specific way. | Organization is essential for life because it allows organisms to function properly. |
| Metabolism | Living organisms take in nutrients and use them to produce energy and build new molecules. | Metabolism is essential for life because it provides organisms with the energy and materials they need to survive. |
| Responsiveness | Living organisms respond to their environment by changing their behavior or physiology. | Responsiveness is essential for life because it allows organisms to adapt to their environment and survive. |
| Growth | Living organisms grow and develop over time. | Growth is essential for life because it allows organisms to reach their full potential and reproduce. |
| Reproduction | Living organisms reproduce, creating new individuals that are similar to themselves. | Reproduction is essential for life because it ensures the continuation of the species. |
The properties of life are interconnected. For example, metabolism provides the energy that organisms need to grow and reproduce. Responsiveness allows organisms to adapt to their environment and obtain the resources they need to survive. Growth and reproduction ensure the continuation of the species.
Biological Molecules
Biological molecules are the building blocks of life. They are large, complex molecules that are essential for the structure and function of cells.
The four main types of biological molecules are:
- Carbohydrates
- Lipids
- Proteins
- Nucleic acids
Carbohydrates are used for energy and storage. Lipids are used for energy storage and insulation. Proteins are used for structure, function, and regulation. Nucleic acids are used for storing and transmitting genetic information.
Biological molecules interact with each other to form complex structures. For example, proteins and lipids form cell membranes. Carbohydrates and proteins form glycoproteins. Nucleic acids and proteins form chromosomes.
Metabolism
Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in a living organism. It is essential for life because it provides organisms with the energy and materials they need to survive.
The two main types of metabolism are:
- Catabolism
- Anabolism
Catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler molecules. Anabolism is the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler molecules.
Metabolism is regulated by a variety of factors, including hormones, enzymes, and feedback loops.
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable internal environment in an organism. It is essential for life because it allows organisms to function properly.
Organisms maintain homeostasis by using a variety of mechanisms, including:
- Negative feedback loops
- Positive feedback loops
- Hormonal regulation
Negative feedback loops are the most common type of homeostatic mechanism. In a negative feedback loop, a change in the internal environment triggers a response that brings the environment back to its normal state.
Positive feedback loops are less common than negative feedback loops. In a positive feedback loop, a change in the internal environment triggers a response that amplifies the change.
Hormonal regulation is another important mechanism for maintaining homeostasis. Hormones are chemical messengers that are produced by glands and travel through the bloodstream to target cells.
Evolution: The Properties Of Life Mastering Biology
Evolution is the change in the genetic composition of a population over time. It is driven by natural selection, which is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals with favorable traits.
There is a wealth of evidence for evolution, including:
- The fossil record
- Comparative anatomy
- Molecular biology
Evolution has implications for our understanding of life. It helps us to understand how organisms have changed over time and how they are related to each other.
FAQ Summary
What are the three main tenets of the cell theory?
The three main tenets of the cell theory are: 1) All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2) The cell is the basic unit of life. 3) All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
How does metabolism contribute to life?
Metabolism is essential for life because it provides the energy and building blocks that cells need to function. Metabolism involves two main processes: catabolism, which breaks down complex molecules into simpler ones, and anabolism, which builds complex molecules from simpler ones.
What is the importance of homeostasis?
Homeostasis is essential for life because it maintains a stable internal environment within an organism. Homeostasis involves a variety of mechanisms that work together to regulate factors such as temperature, pH, and blood sugar levels.
