Introducing our comprehensive subatomic particles worksheet with answers, an invaluable resource designed to illuminate the enigmatic realm of the tiniest constituents of matter. Delve into the fundamental properties, interactions, and applications of subatomic particles, empowering you with a deeper understanding of the very fabric of our universe.
Subatomic particles, the building blocks of atoms, exhibit a fascinating array of properties and behaviors. Our worksheet provides a detailed exploration of their charge, mass, and spin, equipping you with a solid foundation in their fundamental nature. Additionally, we present a comprehensive table summarizing the key characteristics of protons, neutrons, and electrons, providing a quick reference for easy comprehension.
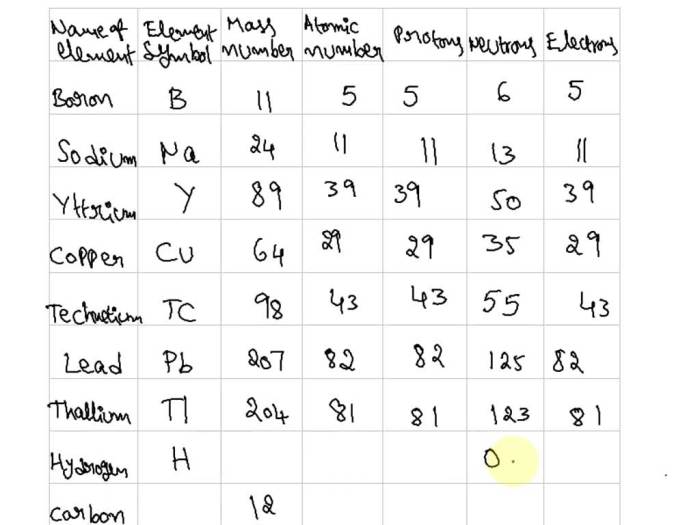
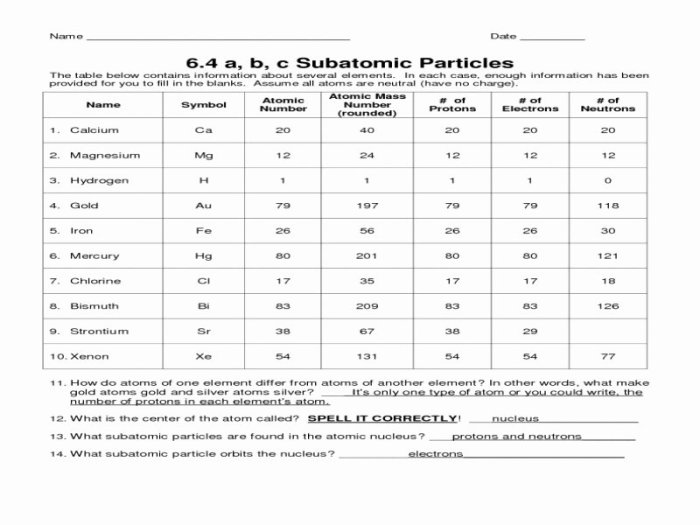
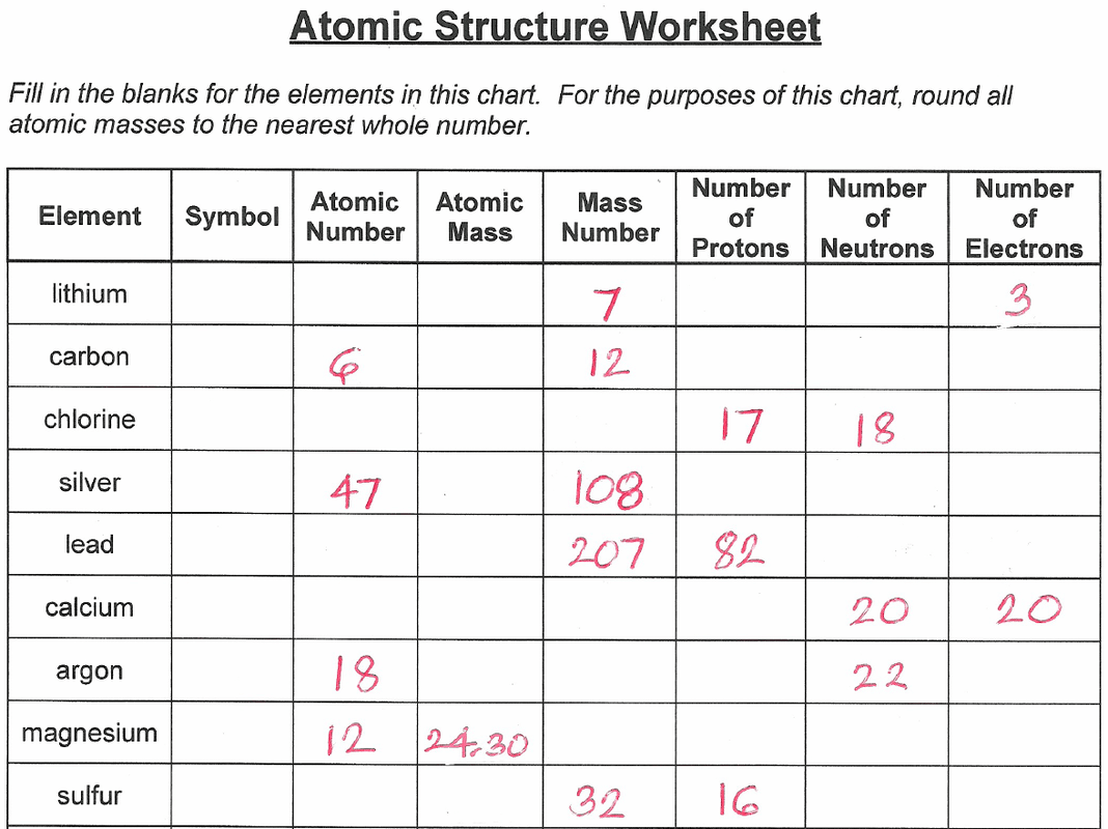
Subatomic Particle Properties
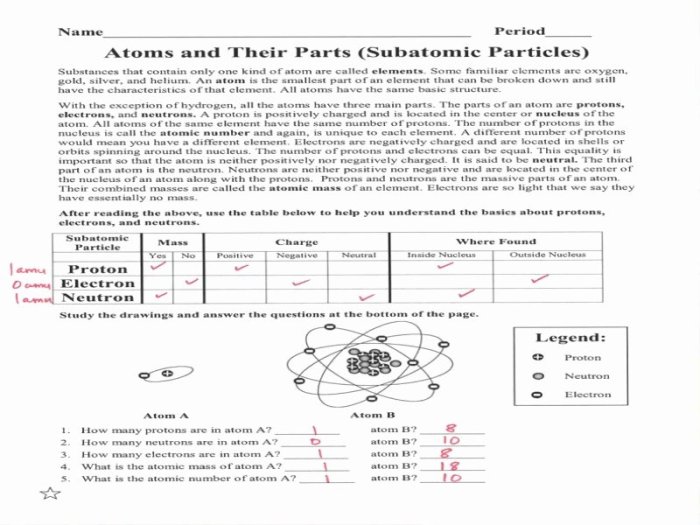
Subatomic particles are the fundamental building blocks of matter. They are extremely small, with masses that are a tiny fraction of an atom’s mass. Subatomic particles have three basic properties: charge, mass, and spin.
Charge refers to the electrical charge of a particle. Protons have a positive charge, electrons have a negative charge, and neutrons have no charge. Mass refers to the amount of matter in a particle. Protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass, which is about 1 atomic mass unit (amu).
Electrons have a much smaller mass, which is about 1/1836 amu.
Spin refers to the intrinsic angular momentum of a particle. Protons and neutrons have a spin of 1/2, while electrons have a spin of 1/2. Spin is a quantum property that can only take on certain discrete values.
Summary of Key Properties of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
| Property | Proton | Neutron | Electron |
|---|---|---|---|
| Charge | +1e | 0 | -1e |
| Mass | 1 amu | 1 amu | 1/1836 amu |
| Spin | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1/2 |
Subatomic Particle Interactions
Subatomic particles interact with each other through three fundamental forces: the strong force, the weak force, and the electromagnetic force.
The strong force is the strongest of the three forces. It is responsible for holding the protons and neutrons together in the nucleus of an atom. The strong force is only effective over very short distances, about the size of an atomic nucleus.
The weak force is responsible for certain types of radioactive decay. It is also involved in the interactions between neutrinos and other particles. The weak force is much weaker than the strong force, but it has a longer range.
The electromagnetic force is responsible for the interactions between charged particles. It is the force that causes electrons to orbit the nucleus of an atom. The electromagnetic force is much weaker than the strong force, but it has a much longer range.
Diagram of Interactions between Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons within an Atom, Subatomic particles worksheet with answers
[Diagram yang menggambarkan interaksi antara proton, neutron, dan elektron dalam sebuah atom]
Subatomic Particle Models
Over the years, scientists have developed a number of models to explain the structure of atoms and the behavior of subatomic particles. Some of the most important models include:
- Rutherford model
- Bohr model
- Quantum mechanical model
Timeline of the Evolution of Subatomic Particle Models
[Timeline yang menunjukkan evolusi model partikel subatomik]
Subatomic Particle Applications: Subatomic Particles Worksheet With Answers
Subatomic particles are used in a variety of technologies, including:
- Nuclear power plants
- Medical imaging
- Particle accelerators
Potential Future Applications of Subatomic Particle Research
Subatomic particle research is a rapidly growing field. Scientists are constantly making new discoveries about the fundamental nature of matter. These discoveries have the potential to lead to new technologies that could revolutionize our world.
Subatomic Particle Detection
Subatomic particles are detected using a variety of techniques, including:
- Cloud chambers
- Bubble chambers
- Scintillation counters
Comparison of Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Detection Methods
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud chambers | – Simple and inexpensive
|
– Limited resolution
|
| Bubble chambers | – High resolution
|
– Complex and expensive
|
| Scintillation counters | – Fast and efficient
|
– Limited resolution
|
Essential FAQs
What are the three main types of subatomic particles?
Protons, neutrons, and electrons
What is the charge of a proton?
+1
What is the mass of a neutron?
Approximately equal to the mass of a proton
What is the role of subatomic particles in nuclear power plants?
They undergo nuclear reactions to generate energy